~Lee Jie Ying (70148)
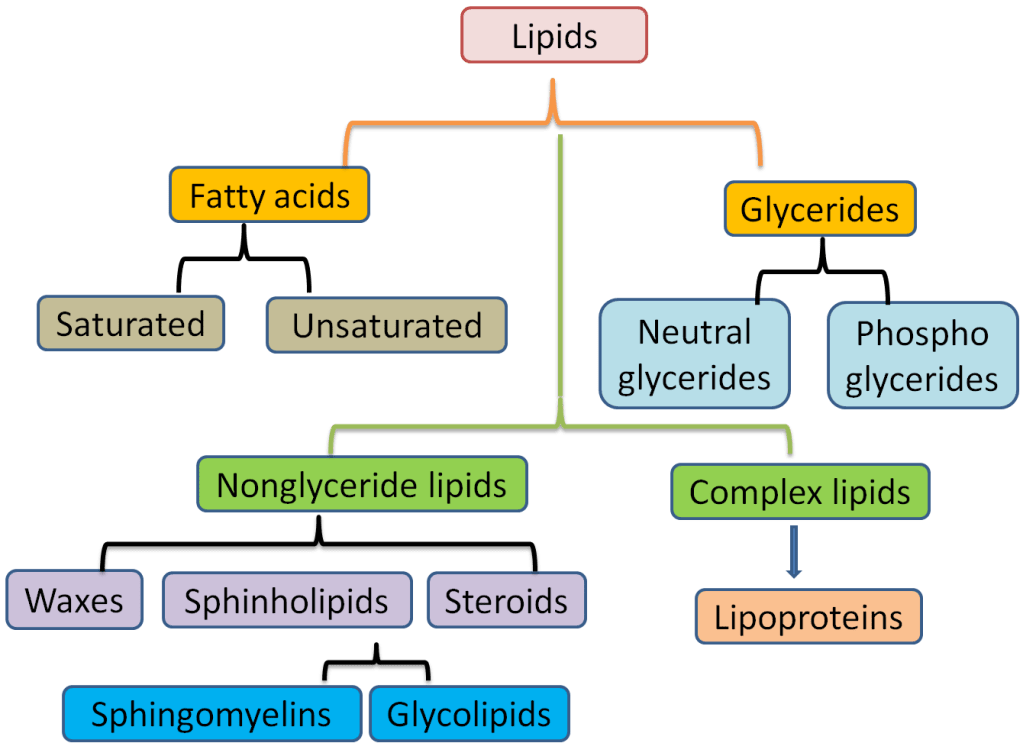
In this topic, I have learnt that lipids are biomolecules that are soluble in organic solvents. There are two types of lipids that are non-polar lipids and polar lipids. Non-polar lipids are act as energy storage and polar lipids are the basis of bilayers. Lipids are classified into several groups that are fatty acids, triacylglycerols, glycerophospholipids, sphingolipids and isoprenoids.
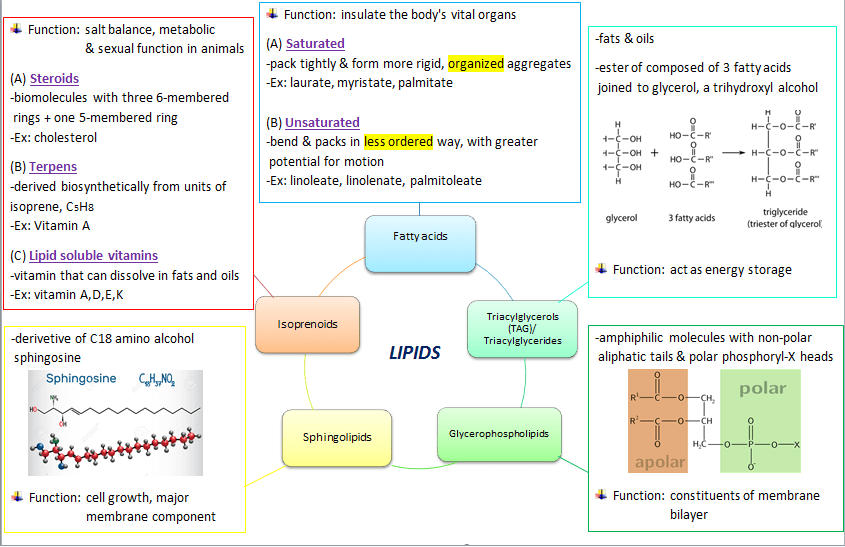
For fatty acids, the predominant fatty acids in plants and animals are C16 and C18. Saturated chains packs tightly and form more rigid, organized aggregates. Unsaturated chains bend and pack in less ordered way, with greater potential for motion.
For triacylglycerols, fatty acids are triesters of glycerol. Most contain two or three different types of fatty acid residues. Animal fats contain high percentage of saturated fatty acids and residues. The melting temperature of fatty TAG varies with degree of saturation and chain length. Triacylglycerols function as energy storage, insulation and saponification. TAG make up more than 95 percent of lipids in the diet and are commonly found in fried foods, vegetable oil, butter, whole milk, cheese, cream cheese, and some meats. Naturally occurring triacylglycerols are found in many foods, including avocados, olives, corn, and nuts.
For phospholipids, it can be degraded at various point, depending on the enzymes used. These enzymes are generally called phospholipase. For sphingolipids, they are derivatives of the C18 amino alcohol sphingosine. The example of sphingolipids are sphingomyelins, cerebrosides and gangliosides.. for steroids, steroids hormones serve many functions in animals which is including salt balance, metabolic and sexual functions.
Glycolipids a large group of sphingolipids, are so called because they contain one or more molecules of sugar (glucose or galactose). Glycolipids, a general property of which is immunological activity, include the cerebrosides, gangliosides, and ceramide oligosaccharides. Of limited distribution in nature, cerebrosides are most abundant in the myelin sheath surrounding nerves. Sulfate-containing cerebrosides, known as sulfatides, occur in the white matter of brain. Gangliosides, most abundant in nerve tissue (especially the gray matter of brain) and certain other tissues (e.g., spleen) are similar to cerebrosides except that, in addition to the sugar component, they contain several other molecules of carbohydrate (N-acetylglucosamine or N-acetylgalactosamine and N-acetylneuramine). Ceramide oligosaccharides also contain several molecules of carbohydrate; an example is globoside from red blood cells.
Isoprenoid any of a class of organic compounds composed of two or more units of hydrocarbons , with each unit consisting of five carbon atoms arranged in a specific pattern. Isoprenoids play widely varying roles in the physiological processes of plants and animals. They also have a number of commercial uses. Isoprenoids in living organisms range in function from pigments and fragrances to vitamins and precursors of sex hormones. One of the most familiar natural substances, rubber, is a polyisoprene. Other commercially valuable isoprenoids are those used as flavourings, solvents, and raw materials for chemicals.
~Kee Bee Hoon (70059)
The next lecture after the topic carbohydrates is the lipids. The definition of lipids is one of the types of biomolecules that are soluble in organic solvents. Based on today’s lessons, I have found out that there are two types of lipids based on their polarity, which is the non-polar lipids (for energy storage) and the polar lipids (as the basis of bilayers). Besides, lipids also can be further classified into five groups, which are fatty acids, triacylglycerols, glycerophospholipids, sphingolipids and isoprenoids.
The mind map displays below is the summary I learned from today’s class. It illustrated on the different types of carbohydrates with their respective functions.
All in all, the lipids are essential for all life on Earth. In my opinion, I think that having a deeper understanding in lipids is important as by doing so, it enables us to know more about the way they function and acts as biological components in our body.
~Chow Ying Qi (69365)
There are 2 types of lipids, the polar and the non-polar lipids. Lipids can also be classified into 5 major groups which are the fatty acids, triglycerol, glycerolphospholipds, sphingolipids and isoprenoids.
For fatty acids, they have a general formula of CH3(CH2)nCOOH, where n usually ranges from 2 to 28 and is always an even number. The carbons that are linked in single bond within the hydrocarbon chain is classified as a saturated fatty acid, while they are classified as unsaturated fatty acids when the hydrocarbon chain has a double bond. In addition to that, if there is just one double bond in a fatty acid, it is classified as monounsaturated fatty acid, while if there are multiple double bonds, it is said to be polyunsaturated fatty acid. Moreover, fatty acids are insoluble in water. For triglycerol,they are non-polar, hydrophobic, and insoluble in water. This is due to the ester linked bond between the polar hydroxyls of glycerol and the polar carboxylates of the fatty acids. Next ,for glycerolphospholipid, it is said to be an amphipathic molecule, having a hydrophobic part and a hydrophilic part. The fatty acid chains (tail) are hydrophobic and do not interact with water, whereas the phosphate-containing group (head) is hydrophilic due to its presence of charge and interacts readily with water. In terms of functional role, glycerolphospholipid is a specialised lipid which made up the majority of cell membrane structure. Lastly, I learnt that sphinholipids are the major membrane components. It act as receptors for pituitary glycoprotein hormones that regulate physiological functions.